Polymers:
Monomers are linked together to form long chains of polymers. It exits a wide diversity of polymers: crystalline, microcrystalline, amorphous.
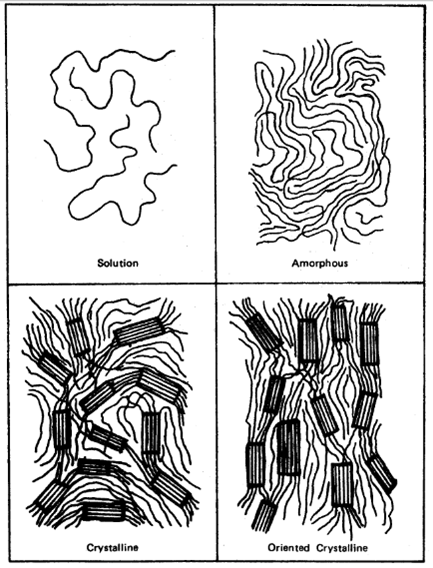
The material we are going to study is the Polyethylene (PE) a semi-crystalline material. It has a lamellar phase (crystalline structure) with amorphous regions between. Polymers films are mainly used the packaging industry
X-rays scattering:
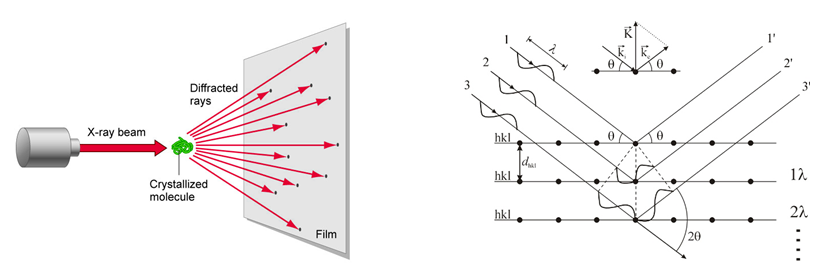
The X-rays scattering method is used to extract information about the structure of a material in dynamic conditions. The beam is diffracted in different directions depending on the atomical plans directions.
In the case of our material the XRS images show the electrons density information.
Data Extraction:
A tensile test where performed on the blown films, while taking in-situ scattering measurements. From this test the stress-strain curves as well as the time resolved XRS images were extracted.
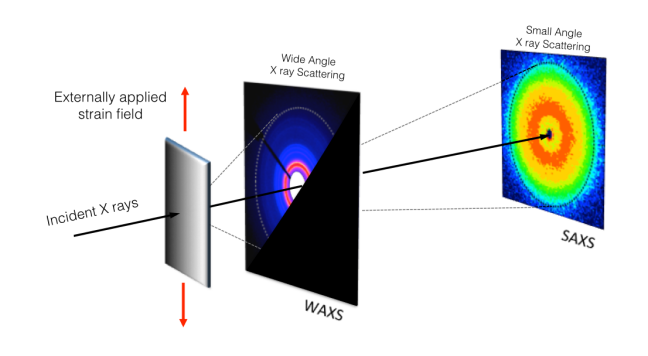
Two types of images can be extrated from the X-rays images. SAXS images (Small Angles X-rays Scattering) whitch in case of our material provides informations on a scale of 1 to 100 nm. WAXS images (Wide Angles X-rays Scattering) on a scale of 0.1 to 10 nm.
Previous Project:
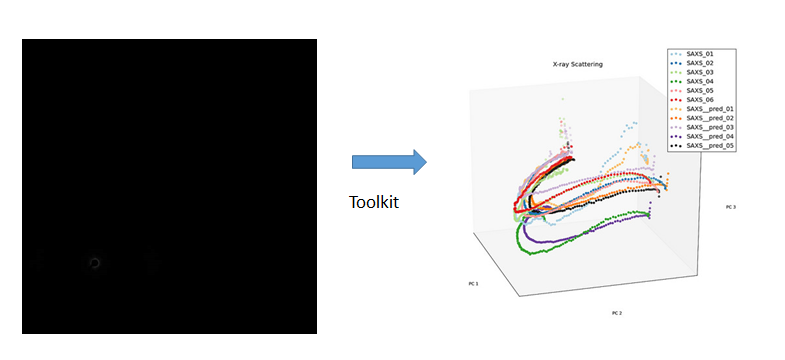
During the last class project, the previous group studied the SAXS images. The goal was to generate a Process-Structure linkage. They created a toolbox that predicts the evolution of the material structure during the tensile test in the PC space.
Sources:
[1]Structure Property Relationship in Polyethylene Blown Films, Abhiram Kannan
[2]Everything SAXS: small angle scattering patterns collection and correction, Brian Richard Pauw